If you're running a business in India and planning to import products, whether it's electronics, machinery, plastics, fabrics, or raw materials, you're stepping into a world full of opportunity. But along with that opportunity comes a maze of rules, licenses, taxes, and government procedures that you can’t afford to ignore.
That’s where understanding India’s import laws and regulations becomes essential.
These laws aren’t just technicalities. They directly affect your profits, delivery timelines, and even your business reputation. If you're a first-time importer or already in the market, knowing the rules helps you avoid delays at customs, unexpected penalties, or legal trouble. More importantly, it helps you build a professional and trustworthy business.
In this blog, we’ll explain why learning about Indian import laws and regulations is so important, what rules and processes you need to follow, and how to stay compliant while growing your import business.
What Are Indian Import Laws and Regulations?
Import laws in India are governed by a range of statutes, rules, and procedures set by the central government through the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), the Customs Department, and other regulatory authorities.
Whether you’re importing goods from the UK or the USA, the law compliance has to be on point.
Some of the key laws include:
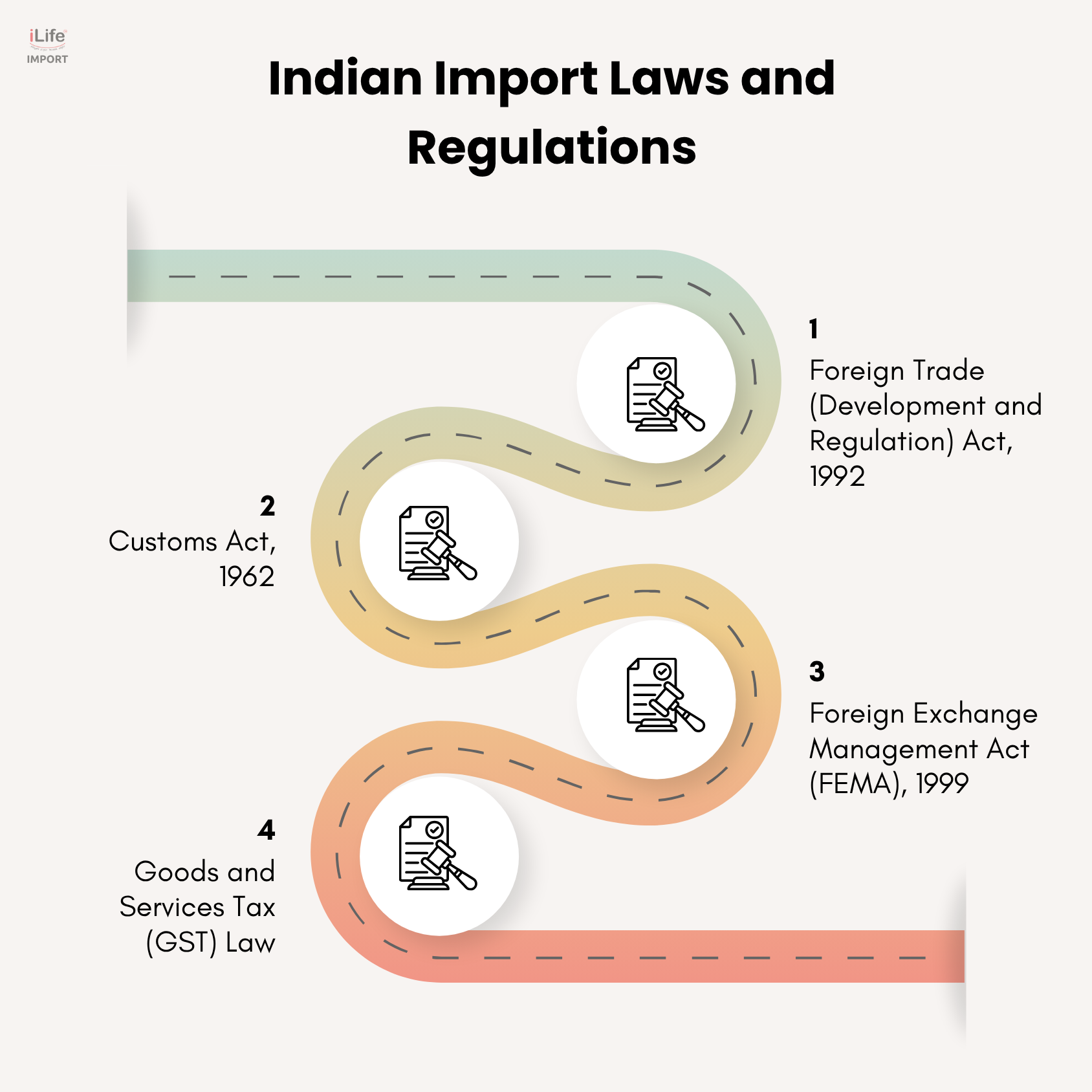

- Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Act, 1992
Governs India's foreign trade by regulating imports and exports through licensing, promoting trade development, and maintaining national economic interests.
Provides a legal framework for the levy, assessment, and collection of customs duties on imported goods and governs customs clearance procedures.
- Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999
Regulates foreign exchange transactions to ensure smooth trade payments, legal forex inflow/outflow, and compliance in cross-border import operations.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Law
Mandates IGST on imported goods, enabling input tax credit for businesses, and a uniform tax structure across states for imports.
These laws and regulations outline procedures for registration, documentation, valuation, classification, restrictions, duties, and regulatory compliance for Indian importers.
For any Indian business looking to import, a strong understanding of these regulations is important to avoid delays, penalties, or seizure of goods.
Now, let’s understand the importance of following legal regulations when sourcing goods from China, for example.
Why Are Import Laws Important for Importers?
Let’s understand the importance of the import laws in India:
a) Legal Protection and Compliance
Understanding the legal rules for importing goods into India ensures that your business operates within the boundaries of the law. Ignorance is not an excuse when it comes to international trade. Misdeclarations, undervaluation, or failure to obtain licenses can lead to fines, legal disputes, or even blacklisting.
b) Smooth Customs Clearance
Indian customs clearance procedures can be intricate, involving various forms, duties, and inspections. When you are aware of the customs rules in India, you can prepare accurate paperwork. From there, you will get timely clearance of goods without unnecessary delays or demurrage charges.
c) Cost Optimization
Compliance is not just about avoiding fines; it can help you save money. Proper classification of goods under the Harmonized System (HS) Code, using applicable exemptions, and availing input tax credits under GST can significantly reduce your cost of imports.
d) Business Credibility
In today's globalized world, suppliers and logistics partners prefer to work with compliant businesses. Understanding import compliance and following it consistently builds a trustworthy reputation and encourages long-term international partnerships.
In essence, knowing the import laws is in favor of your business to manage the import goods very smoothly and without any interruption.
It’s a time to follow the procedures to bring goods from another country to your origin, in India.
Key Aspects of Import Rules and Procedures in India
When importing goods to India from any other country, there are some factors to consider:
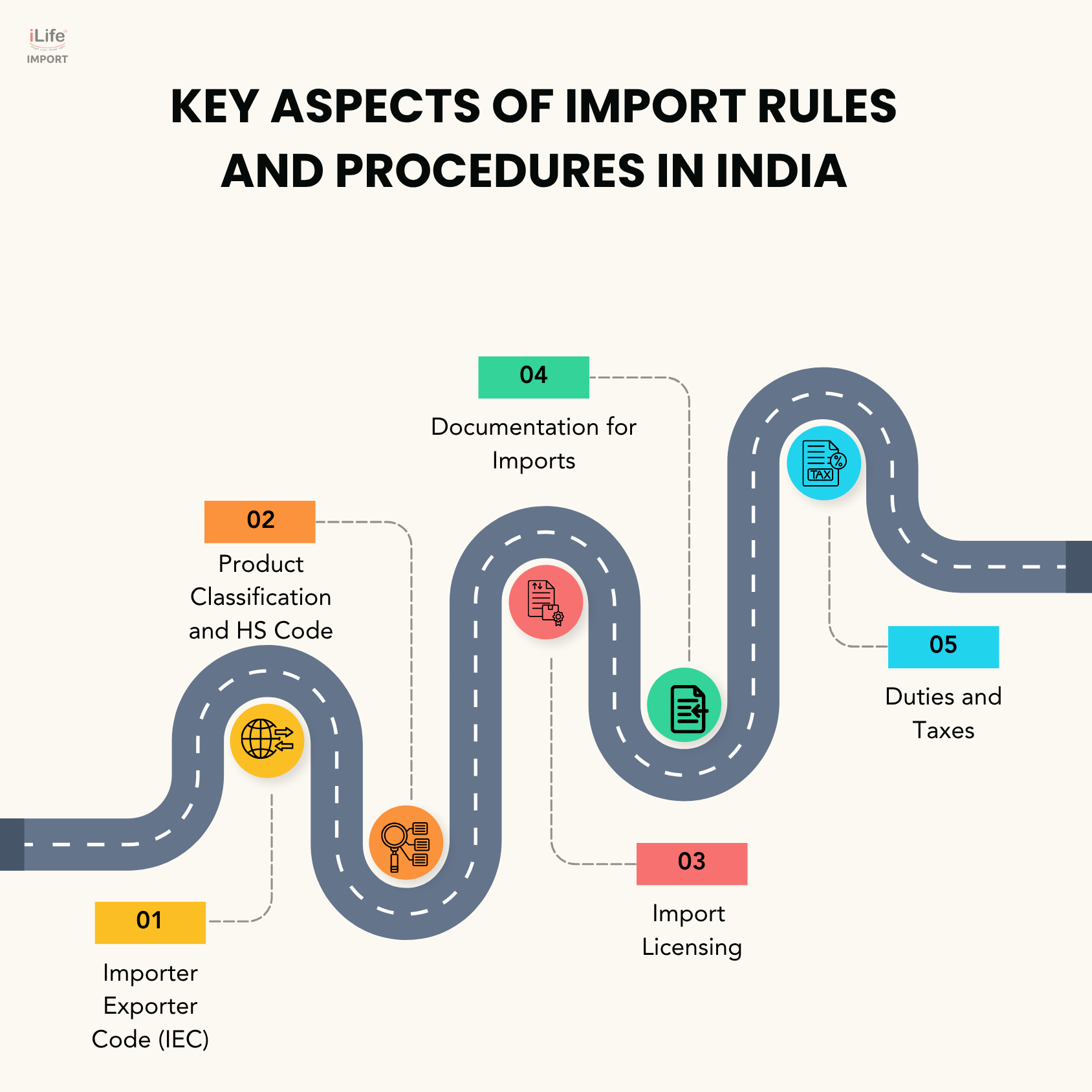
a) Importer Exporter Code (IEC)
The first step for any business that wants to import goods is to obtain an Importer Exporter Code (IEC) from the DGFT. It’s a 10-digit number that is mandatory for clearing goods through customs and conducting transactions with international suppliers.
Suppose you want to import goods from China. For working with the top wholesale suppliers in China, this number will help you to start the trading business with them.
b) Product Classification and HS Code
All imported goods must be classified according to the Harmonized System Code (HS Code). The classification determines the rate of customs duty and the applicability of restrictions or compliance requirements like BIS certification, FSSAI approvals, etc.
c) Import Licensing
In India, not all products are freely importable. Some fall under the restricted or prohibited categories. Importers must check the DGFT's Import Policy and apply for licenses or permissions when necessary, particularly for items like chemicals, electronics, and used machinery.
d) Documentation for Imports
The key documents required for importing goods legally in India, and Indian customs clearance include:
- Commercial Invoice
- Bill of Lading or Airway Bill
- Packing List
- Certificate of Origin
- Bill of Entry
- Insurance Documents
- Import Licenses (if required)
Failure to submit the correct documentation can lead to assessment issues or cargo detention.
e) Duties and Taxes
Importers must pay Basic Customs Duty (BCD), Integrated GST (IGST), Social Welfare Surcharge, and any applicable safeguard or anti-dumping duties. Understanding how duties are calculated based on CIF value and customs valuation rules is critical for accurate costing.
As a business, you have to know the governing bodies in India to regulate safe, fair, and prominent international trading.
Regulatory Bodies That Govern Imports in India
Several government authorities are involved in regulating and monitoring imports:
- Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT): Issues IEC, foreign trade policy, licensing.
- Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC): Enforces customs laws and collects duties.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): Ensures product compliance with safety standards.
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI): Regulates food product imports.
- Plant Quarantine, Animal Quarantine, Drug Controller General of India (DCGI), etc.
Understanding which body governs your product category can save you from last-minute surprises during clearance.
Knowing the mistakes importers make helps you to save the goods from being seized at the ports and a heavy fine imposed.
4 Common Mistakes Indian Importers Make (And How to Avoid Them)
Most first-time importers make mistakes when sourcing the goods:

a) Ignoring Pre-Shipment Compliance
Many importers assume compliance starts after the shipment reaches India. In reality, understanding Indian import regulations for business requires that you prepare before the goods are even dispatched. For example, certifications or labeling rules must be completed at the origin.
So, basically, it’s not enough to have the best shipping methods for importing goods. But with that, you have to follow the regulations for international trading as well.
b) Misclassifying Goods
Assigning the wrong HS code can lead to underpayment or overpayment of duties. Use professional services or consult customs brokers to ensure correct classification and valuation.
c) Suspicious Vendor Due Diligence
Working with unverified overseas suppliers can expose you to risks like poor-quality goods, shipping scams, or documentation fraud. These are scams related to importing goods from China to India. Always verify exporter credentials, especially when importing from countries like China.
d) Not Factoring in All Duties and Charges
Businesses budget only for basic customs duty but fail to include cess, GST, logistics, port handling, and clearance charges, leading to a profit cut. So, don’t make this mistake if the business is currently compromising its cash flow.
Don’t know the best way to get the trade completion safely. The next section will answer.
How to Ensure Import Compliance in India?
When you import goods to India, follow the compliance mentioned below:
a) Stay Updated with Policy Changes
India’s import regulations can change based on economic conditions, trade relations, or policy shifts. Subscribe to DGFT notifications, customs circulars, and GST updates.
b) Work with Professionals
Hiring a CHA (Customs House Agent), freight forwarder, or import consultant can help ensure the smooth handling of documentation, classification, and clearance. Don’t be confused between freight forwarding and the direct shipping method. Pick the relevant one as per the goods' value and conditions.
c) Use Digital Systems
Make use of online platforms such as ICEGATE (Indian Customs EDI Gateway), DGFT portal, and the SWIFT system to streamline compliance and documentation processes.
d) Keep Records
Maintain proper records of all imports for a minimum of 5 years to stay compliant with audits and regulatory scrutiny.
Benefits of Understanding Indian Import Laws and Regulations
Knowing the import rules and procedures in India isn’t just about ticking legal boxes; it brings tangible benefits:
- Predictable Delivery Timelines: Reduced chances of customs hold-ups.
- Cost Control: Lower duties through correct classification and tax benefits.
- Risk Mitigation: Fewer chances of non-compliance penalties or cargo seizures.
- Improved Supplier Relations: Confidence among international partners.
- Scalability: Ready to grow your import volumes without hurdles.
Final Thoughts
To be successful in today’s global trade environment, Indian businesses must move beyond basic procurement strategies and dive into the legal and regulatory aspects of importing. Whether you're importing for the first time or scaling your operations, understanding Indian import laws and regulations gives you a solid foundation to build a sustainable and compliant business.
Remember, international trade is full of opportunities. But only those who navigate the legal framework wisely can truly capitalize on them.
FAQs
- Do I need an Importer Exporter Code (IEC) to import goods into India?
Yes, IEC is mandatory for all importers and exporters in India. This code will help importers get help with customs clearance in India without any interruption.
- How do I know if a product needs an import license?
Check the DGFT’s Import Policy and look for your product under the HS code. Restricted items need licenses. For that, it’s good to consult an import service provider to manage the entire shipping process.
- What is the role of customs brokers in import compliance?
They help classify goods correctly, prepare documents, calculate duties, and ensure smooth customs clearance. With their expert service, there are fewer chances to hold the entire container on custom hold.
- Can I import goods without paying GST?
No, you cannot. In India, all imported goods are subject to Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) at the time of import. However, if you're a GST-registered business, you can usually claim an Input Tax Credit (ITC) on the IGST paid, reducing your overall tax liability.
- What happens if I fail to comply with import regulations?
If you can’t follow the import regulations, it results in penalties, including fines, detention of goods, cancellation of IEC, and prosecution under customs law.
- Need Help with Import Compliance?
If you're unsure about navigating import laws or handling documentation, iLife Import can guide you through every step from sourcing and customs to final delivery. Let us help you import smarter, faster, and fully compliant.
Contact us now at your convenience. We’re not just promising results. We are experts who are familiar with the import regulations in India and ensure your goods safely reach your doorsteps.